All Packages Class Hierarchy This Package Previous Next Index
java.lang.Object
|
+----java.awt.BorderLayout
North, South, East,
West, and Center. When adding a
component to a container with a border layout, use one of these
five names, for example:
Panel p = new Panel();
p.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
p.add(new Button("Okay"), "South");
As a convenience, BorderLayout interprets the absence of a string
specification the same as "Center":
Panel p2 = new Panel();
p2.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
p2.add(new TextArea()); // Same as p.add(new TextArea(), "Center");
The components are laid out according to their
preferred sizes and the constraints of the container's size.
The North and South components may
be stretched horizontally; the East and
West components may be stretched vertically;
the Center component may stretch both horizontally
and vertically to fill any space left over.
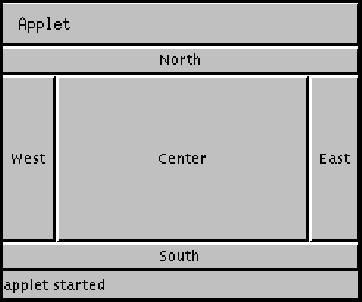
Here is an example of five buttons in an applet laid out using
the BorderLayout layout manager:

The code for this applet is as follows:
import java.awt.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
public class buttonDir extends Applet {
public void init() {
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add("North", new Button("North"));
add("South", new Button("South"));
add("East", new Button("East"));
add("West", new Button("West"));
add("Center", new Button("Center"));
}
}
target container
using this layout manager.
target
container using this layout manager, based on the components
in the container.
public static final String NORTH
public static final String SOUTH
public static final String EAST
public static final String WEST
public static final String CENTER
public BorderLayout()
public BorderLayout(int hgap,
int vgap)
hgap
and the vertical gap is specified by vgap.
public int getHgap()
public void setHgap(int hgap)
public int getVgap()
public void setVgap(int vgap)
public void addLayoutComponent(Component comp,
Object constraints)
"North",
"South", "East",
"West", or "Center".
Most applications do not call this method directly. This method
is called when a component is added to a container using the
Container.add method with the same argument types.
public void addLayoutComponent(String name,
Component comp)
addLayoutComponent(Component, Object).
public void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp)
remove or
removeAll methods. Most applications do not call this
method directly.
public Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container target)
target container
using this layout manager.
This method is called when a container calls its
getMinimumSize method. Most applications do not call
this method directly.
public Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container target)
target
container using this layout manager, based on the components
in the container.
Most applications do not call this method directly. This method
is called when a container calls its getPreferredSize
method.
public Dimension maximumLayoutSize(Container target)
public float getLayoutAlignmentX(Container parent)
public float getLayoutAlignmentY(Container parent)
public void invalidateLayout(Container target)
public void layoutContainer(Container target)
This method actually reshapes the components in the specified
container in order to satisfy the constraints of this
BorderLayout object. The North
and Southcomponents, if any, are placed at
the top and bottom of the container, respectively. The
West and East components are
then placed on the left and right, respectively. Finally,
the Center object is placed in any remaining
space in the middle.
Most applications do not call this method directly. This method
is called when a container calls its doLayout method.
public String toString()
All Packages Class Hierarchy This Package Previous Next Index