|
|
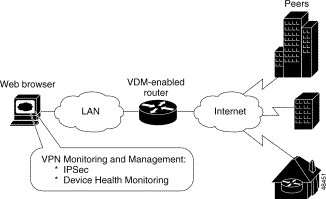
VPN Device Manager (VDM) software is installed directly onto VPN-enabled Cisco routers. It allows network administrators to manage and configure site-to-site VPNs on a single router from a web browser. VDM implements a wizard-based GUI that allows simplified VPN configuration of the router. VDM requires configuration of some Cisco IOS commands before it can be fully operational. VDM is supported on Cisco IOS release 12.1(6)E or later. For information about new features in the VDM 1.1 release, see the "New Features" section.
VDM supports site-to-site VPNs. Its step-by-step wizards simplify the configuration of common VPN setups, interfaces, and policies, including:
VDM also monitors general system statistics and VPN-specific information such as tunnel throughput and errors. The graphing capability allows comparison of such parameters as traffic volume, tunnel counts, and system utilization.
Figure 1 shows a simplified VDM deployment.
This document contains:
VDM release 1.1 supports the Secure HTTP (HTTPS) feature. This feature provides the capability to connect to the Cisco IOS HTTPS server securely. HTTPS is supported on Cisco IOS release 12.1(11)E or later.
 |
Note Although every effort has been made to validate the accuracy of the information in the printed and electronic documentation, you should also review the VDM documentation on Cisco.com for any updates. |
Use these publications to learn more about VDM:
The VDM online help contains some options for clearing active tunnels. In addition to using those options, you can clear all active IPSec and IKE tunnels by clicking the Clear IPSec and IKE Tunnels button in the Clear Active Tunnels dialog box.
This section contains:
Table 1 contains detailed descriptions of VDM benefits.
Configuration Wizards | VDM browser-based wizards help you perform ordinarily complex setup operations including:
|
Convenient Navigation | The following navigation methods ensure that you can identify your current location within each wizard:
|
Monitoring Functions | Monitored data in graphs and charts contains basic router information, a VPN report card, top-ten lists, and detailed views of user-specified tunnels monitoring including:
|
No Client Installation | You can run VDM from a browser without installing it on the computer. |
Preview of CLI Commands Generated by the Wizards | The View CLI button within the Configure secondary menu enables you to view the exact Cisco IOS CLI commands to be executed after you commit your configuration. |
Single Device Configuration | Configures only the router from which VDM is launched. Does not read or write configuration information to or from other routers. |
Support for HTTPS Server | Provides the capability to connect to the Cisco IOS HTTPS server securely. |
Table 2 contains supported hardware, software, and memory system requirements.
Supported hardware |
|
Supported software |
|
Available Memory |
|
Table 3 contains browser requirements.
 |
Caution Although VDM might run on any web browser that supports Java and JavaScript, it has been tested only on those listed in this section. It is highly recommended that you use a supported browser. Cisco Systems does not guarantee support for other browsers. |
| Browser | Version | JVM1 | Platform |
|---|---|---|---|
Internet Explorer (recommended) | 5.0 or later | 5.0.0.3309 or later | Windows 2000 with Service Pack 1, Windows NT 4.0 with Service Pack 6a, Windows 98 |
Navigator | 4.7x or later | — | Windows 2000 with Service Pack 1, Windows NT 4.0 with Service Pack 6a, Windows 98, Solaris 2.6 or Solaris 7 |
| 1 JVM=Java Virtual Machine |
This release of VDM does not support:
To install VDM, follow the instructions in the following sections:
 |
Note Effective with Cisco IOS Release 12.1(6)E, all 7100 and 7200 routers can be ordered with VDM preinstalled. If VDM is already installed on your router, go to "Enabling VDM" section. |
If VDM is not installed in your router Flash memory, you must do both of the following:
To download and install VDM:
Step 1 Enter http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/vdm in your browser.
Step 2 Click vdm-1.0.tar to download the file and save it on a TFTP or FTP server.
 |
Note Do not extract the tar file. |
Step 3 Log in to the router directly or use Telnet.
Step 4 Enter enable mode:
Router>enable
Password: xxxxx
Router#
 |
Note In these examples, VDM is installed in disk0:. You can replace disk0: with the correct location (slot1:, slot0:, or disk1:). |
Step 5 Enter the show xsm version command to verify that one of the Cisco IOS releases mentioned in Table 2 is running:
Router>show xsm version
If the appropriate Cisco IOS release is not running, upgrade to the appropriate release.
Step 6 Ensure that the router has at least the minimum required Flash memory (2 MB) by using the directory command to determine the amount of free space, for example:
Router#directory disk0:Directory of disk0:/
1 -rw- 448893 Jan 03 2000 18:06:17 file01.txt
2 -rw- 213273an 03 2000 18:06:17 file02.txt
20578304 bytes total (19733404 bytes free)
Step 7 Do one of the following:
Router#copy tftp://tftp-host/path_to_vdm-1.0.tar/vdm-1.0.tar disk0:/vdm.tarRouter#copy ftp://ftp-host/path_to_vdm-1.0.tar/vdm-1.0.tar disk0:/vdm.tar |
Note File must be named vdm.tar and must be located in the root directory of the Flash device. |
Before using VDM, you must do the following to enable it:
Step 1 Enter config mode:
Router>enablePassword: xxxxxRouter#configure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL-Z.Step 2 Do one of the following:
Router(config)#ip http serverRouter(config)#ip http secure-serverRouter(config)#ip http serverRouter(config)#ip http secure-server
Step 3 Enable XSM by entering:
Router(config)#xsm
Step 4 Enable the XSM history command to track historical VDM statistics by entering:
Router(config)#xsm history vdm
Step 5 Enable the EDM history command to track embedded router statistics by entering:
Router(config)#xsm history edm
Step 6 Enable TopN processing by entering (you could specify the processing intervals from 60 to 86400 seconds):
Router(config)#cry mib topn interval 60
VDM privilege levels control your access to VDM functionality. They control access to VPN configuration information and wizards and are set and changed using XSM privilege commands in the CLI. These commands limit your ability to configure wizards and monitor data only in the VDM GUI. They have no effect on your authorization to configure the router using the CLI. For information about the XSM privilege level commands, see Cisco IOS Commands for VPN Device Manager.
The three privilege levels are:
Authorized to view configuration and monitor dataMonitoring privileges only (monitor users) Unauthorized to use VDMThis section contains:
The VDM URL defaults to configuration mode (default privilege level 15). At this level, you can start VDM using either the HTTP or the HTTPS server. The following sections provide more information:
To start VDM in configuration mode using the HTTP server, do one of the following:
You can connect to the router using any IP address configured on the router. If your router hostname is in the Domain Name System (DNS), you can use the router name instead. For example, if your DNS hostname is charlie and your domain name is anydomain, enter:
http://charlie.anydomain.com/level/1/go/vdm
HTTPS is supported on Cisco IOS release 12.1(11)E or later. To start VDM in configuration mode using the HTTPS server, do one of the following:
You can connect to the router using any IP address configured on the router. If your router hostname is in the Domain Name System (DNS), you can use the router name instead. For example, if your DNS hostname is charlie and your domain name is anydomain, enter:
https://charlie.anydomain.com/level/1/go/vdm
The HTTPS server looks for vdm.tar in all Flash filesystems and the VDM application window appears, see Figure 2.
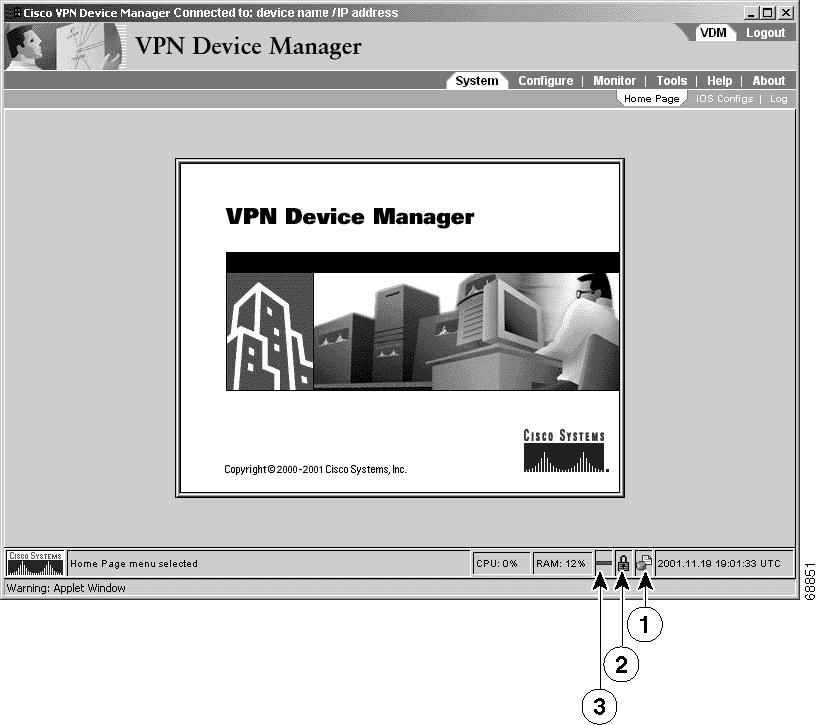
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Authorization icon in configuration mode—Indicates that you can configure the router, view router configuration, and monitor the router. For more information, see the "Understanding VDM Privilege Levels" section. |
2 | Security icon—Closed padlock (Figure 2) indicates that VDM is connected to the router through HTTPS. Open padlock indicates that VDM is connected to the router through HTTP. |
3 | Connection icon—Solid green line indicates that you are connected to the router. Broken red line indicates that you are not connected to the router. |
If VDM displays less information in the various VDM windows than you expected, your privilege level might be set too low. For information about setting the appropriate privilege level, see the "Understanding VDM Privilege Levels" section or ask your system administrator for assistance. For more information, see the VDM online help.
If you do not have configuration mode privileges, you will not be able to configure the router from VDM. However, you can still start VDM (for monitoring purposes) by manually entering your privilege level number in the browser. At this level, you can start VDM using either the HTTP or the HTTPS server. The following sections provide more information:
To start VDM in monitor mode using the HTTP server, enter:
http:// router/level/n/go/vdm
For n, enter a number between 0 and 14. If your number is equal to or greater than the configured VDM monitor mode, and less than the configured VDM configuration mode, you can launch VDM in monitor mode. If not, you will be notified that you do not have the correct privilege level.
You can connect to the router using any IP address configured on the router. If your router hostname is in the Domain Name System (DNS), you can use the router name instead. For example, if your DNS hostname is charlie and your domain name is anydomain, enter:
http://charlie.anydomain.com/level/1/go/vdm
HTTPS is supported on Cisco IOS release 12.1(11)E or later. To start VDM in monitor mode using the HTTPS server, enter:
https://router/level/n/go/vdm
For n, enter a number between 0 and 14. If your number is equal to or greater than the configured VDM monitor mode, and less than the configured VDM configuration mode, you can launch VDM in monitor mode. If not, you will be notified that you do not have the correct privilege level.
You can connect to the router using any IP address configured on the router. If your router hostname is in the Domain Name System (DNS), you can use the router name instead. For example, if your DNS hostname is charlie and your domain name is anydomain, enter:
https://charlie.anydomain.com/level/1/go/vdm
If the HTTPS server finds vdm.tar in the Flash filesystem, it will launch VDM and the VDM application window appears, see Figure 3.
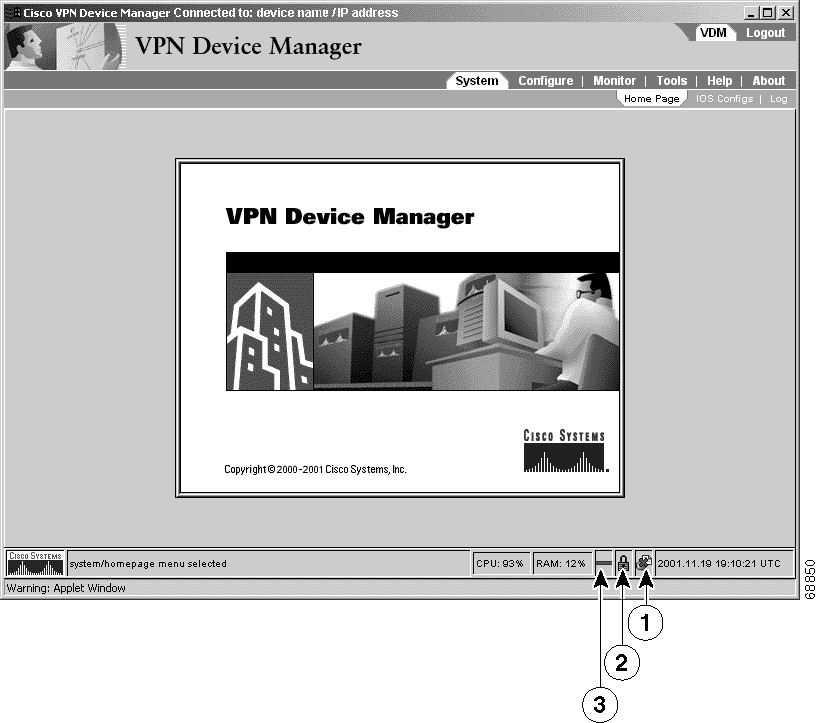
| Number | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Authorization icon in monitor mode—Indicates that you can view monitored router data but you cannot configure the router. For more information, see the "Understanding VDM Privilege Levels" section.
| ||
2 | Security icon—Closed padlock (Figure 3) indicates that VDM is connected to the router through HTTPS. Open padlock indicates that VDM is connected to the router through HTTP. | ||
3 | Connection icon—Solid green line indicates that you are connected to the router. Broken red line indicates that you are not connected to the router. |
If VDM displays less information in the various VDM windows than you expected, your privilege level might be set too low. For information about setting the appropriate privilege level, see the "Understanding VDM Privilege Levels" section or ask your system administrator for assistance. For more information, see the VDM online help.
There are two ways to exit VDM:
To disable VDM, Telnet to the router and enter:
Router>enable
Password:xxxxx
Router#configure terminal
Enter configuration command, one per line. End with CNTL-Z
Router#no xsm
This command disables VDM from the router. You can still run VDM from the client but without the ability to collect data. For uninstallation instructions, see "Uninstalling VDM."
To uninstall VDM, delete the file from the router Flash memory.
Step 1 Telnet to the router and enter:
Router>enable
Password:xxxxx
Step 2 Navigate to disk0: or the directory in which the vdm.tar file is located:
Router#cd disk0:
Step 3 Delete the vdm.tar file using the delete command:
Router#del vdm.tar
Known problems (bugs) in VDM software releases are graded according to severity level. These release notes contain descriptions of:
You can search for problems using the Cisco bug tracking tool, Bug Navigator II. To access Bug Navigator:
Step 1 Log into Cisco.com.
Step 2 Select Service & Support>Technical Support Help—Cisco TAC>Tool Index.
Step 3 In the Jump to: links at the top of the page, click the letter S.
Step 4 Select Software Bug Toolkit/Bug Watcher>Bug Navigator II.
You can also access Bug Navigator by entering the following URL in your web browser: http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/Bugtool/launch_bugtool.pl.
Table 4 describes the problems known to exist in this release.
| Bug ID | Summary | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
CSCdv36863 | VDM does not work with Navigator 6.0 or later. | Navigator 6.0+ is not yet supported. Please use Navigator 4.7+ or Internet Explorer 5.5+. |
CSCdw89882 | An exception occurs when VDM is launched with Navigator on Windows 98. | When using VDM with Navigator 4.76 on Windows 98, you might see errors on the status bar and in the system log about duplicate attributes. No workaround available; exit VDM and restart. |
CSCdw62593 | Enrollment updates are slow in the certificate wizard. | When you use the certificate enrollment wizard in Navigator 4.76 with an HTTPS connection, you might experience updating delays in each step of the wizard. No workaround available; simply wait for the next update of VDM (within 10 seconds). |
CSCdw59489 | Updated data in the table is not sorted correctly on the SystemView: Network Interfaces dialog box. | When viewing the SystemView: Network Interfaces dialog box, you can sort the table by any column. However, after each update, the data is not sorted correctly. To work around this problem, click on the column header of the data after each update to sort the table again. |
CSCdv38482 | Sometimes, VDM reports a parser error, then fails fatally. | No workaround available; exit VDM and restart. |
CSCdw70703 | IPSec Total Throughput chart displays negative values. | Charting the IPSec Total Throughput may intermittently show spikes of negative values. No workaround available. |
CSCdw53247 | VDM displays TopN data even though the TopN system is not enabled on the device. VDM provides no way of allowing the user to determine whether TopN has been enabled. | Before viewing TopN data on VDM, enable the TopN system on the device using the following CLI command: This causes the TopN system to be enabled until you explicitly disable it using the following CLI command: |
CSCdv59589 | VDM displays 3DES as a potential transform even though the IOS image might not support 3DES. | Select 3DES as a transform only if your IOS image supports 3DES. 3DES is supported in the "k2" IOS feature set. |
CSCdt59899 | If you relaunch VDM in the same browser, you might see some exceptions in the Java console. | Before relaunching VDM in the same browser, give the previous VDM application instance enough time to shut down properly. Typically, this is 30 seconds or less. After that, you can relaunch VDM without problems. |
CSCdt51119 | Protocol Profile viewing problem: Deny Some with tcp or udp doesn't work. | In the Connection wizard, selecting Deny Some protocols/services and then specifying tcp or udp fails to generate correct CLI and will not commit successfully. Further, if the correct CLI is manually entered, VDM will not recognize it as an editable connection. To work around this problem, do not use 'Deny Some' with 'tcp' or 'udp' protocols. Using tcp or udp with specific ports works correctly. |
CSCdt53856 or CSCdu06036 | Fatal Error (parser): Transform set name with &. | Double quotes (") or ampersands (&) in the Cisco IOS configuration might cause the GUI to log parser errors, such as To work around this problem, remove any ampersands or double quotes from the router configuration before running VDM. Check all crypto-map names and descriptions, access list names and comments, peer keys and transform set names. |
CSCdt59736 | LZ compression should be disabled when router has ISA or ISM in it. | Routers with Integrated Services Adapter (ISA) or Integrated Services Module (ISM) do not support LZ compression. Transforms with LZ compression selected will fail to commit, and connections that define new transforms with LZ compression will not commit. To work around this problem, do not specify LZ compression in a transform if your router does not support this feature. |
CSCdt66389 | | This can occur with more than 6 charts open at once for long periods of time. To work around this problem, limit your chart usage to six at a time and close any unnecessary charts. |
CSCdt68379 | GUI should correct subnet/mask incongruencies. | Subnets specified in a connection appear to change once committed, but the packets are correctly selected. The router will mask out bits in the netmask that are used. For example, if the IP address 1.2.3.4 and mask 255.255.255.0 are chosen, the Cisco IOS in the router will record this as 1.2.3.0 with a mask of 255.255.255.0. An address of 1.2.3.4 with a netmask of 0.0.0.0 will be displayed as 'any'. No workaround available since this is expected behavior. |
CSCdt71760 | Remove button should not be allowed on unsupported configuration. | A connection might appear in the connection wizard marked with a red-slash-in-a-circle with descriptive text 'on no interface', but if the connection is removed, the commit fails to remove the connection with the error 'crypto map is in use'. This occurs when a connection is attached to a sub-interface. VDM does not recognize sub-interfaces, and erroneously shows those connections as No workaround available. |
CSCdt75160 | A pop-up dialog box requesting "level 15" login and password appears when using ping or traceroute under Tools/Test > Connectivity. | Occurs when logged in under monitor mode. The level 15 login and password is erroneously required to use the ping and traceroute facility from the GUI. There is no workaround available. |
CSCdt77038 | The Connection wizard suffers delays in recognizing access lists. | Under Configure > Connections, some access lists (ACLs) are not recognized for up to 10 seconds. To work around this problem, click on a tab to go to another window. |
CSCdt77127 | Single protocol has been displayed multiple times. | The same protocol or service might be displayed several times in the Description box in the Connection Overview window. No workaround available; the extra entries are harmless. |
CSCdt80364 | Cannot edit a newly created connection after you log in again. | After editing a connection, but before committing it, a dialog box might appear indicating that the connection configuration has changed, and asks if you want to use their new configuration (and discard yours), but no one has changed the configuration. To work around this problem, choose No to preserve your changes, and commit as usual. |
CSCdt91013 | VDM: turn on/off | Turning XSM history on/off while charting causes an exception. The charting tools use historical data from the router and disabling it while the chart is running may cause a problem. To work around this problem, do not disable XSM history while using the charting tools. |
CSCdt95961 | Greater than four XSM sessions cause the client to fail to get a connection. | When running four or more simultaneous VDM clients, the last client to connect may fail to connect to the router and does not reconnect, or it appears to connect with a session ID of 0. To work around this problem, exit and restart VDM on the client with the failed connection or wait until one or more of the other clients has disconnected. The number of active VDM clients can be verified on the router using the |
CSCdu07875 | Reload while VDM up exception. | Reloading the router while running VDM causes an exception. VDM occasionally cannot automatically reconnect to the router after it is reloaded and throws an exception. When this happens VDM must be restarted. |
CSCdu09119 | NullPointerException when exiting VDM. | Closing VDM using the [X] in the window frame instead of Logout might generate an exception. No workaround available. |
CSCdu09191 | Log Error: attribute is defined more than once. | The log displays errors involving multiple definitions of attributes. Attributes are defined to hold data from the router. Multiple definitions are harmless. No workaround is necessary. |
The following sections explain how to obtain documentation from Cisco Systems.
You can access the most current Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at the following URL:
Translated documentation is available at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Cisco documentation is available in the following ways:
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on Cisco.com, you can submit technical comments electronically. Click Feedback at the top of the Cisco Documentation home page. After you complete the form, print it out and fax it to Cisco at 408 527-0730.
You can e-mail your comments to bug-doc@cisco.com.
To submit your comments by mail, use the response card behind the front cover of your document, or write to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Document Resource Connection
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883
We appreciate your comments.
Cisco provides Cisco.com as a starting point for all technical assistance. Customers and partners can obtain documentation, troubleshooting tips, and sample configurations from online tools by using the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) Web Site. Cisco.com registered users have complete access to the technical support resources on the Cisco TAC Web Site.
Cisco.com is the foundation of a suite of interactive, networked services that provides immediate, open access to Cisco information, networking solutions, services, programs, and resources at any time, from anywhere in the world.
Cisco.com is a highly integrated Internet application and a powerful, easy-to-use tool that provides a broad range of features and services to help you to
You can self-register on Cisco.com to obtain customized information and service. To access Cisco.com, go to the following URL:
The Cisco TAC is available to all customers who need technical assistance with a Cisco product, technology, or solution. Two types of support are available through the Cisco TAC: the Cisco TAC Web Site and the Cisco TAC Escalation Center.
Inquiries to Cisco TAC are categorized according to the urgency of the issue:
Which Cisco TAC resource you choose is based on the priority of the problem and the conditions of service contracts, when applicable.
The Cisco TAC Web Site allows you to resolve P3 and P4 issues yourself, saving both cost and time. The site provides around-the-clock access to online tools, knowledge bases, and software. To access the Cisco TAC Web Site, go to the following URL:
All customers, partners, and resellers who have a valid Cisco services contract have complete access to the technical support resources on the Cisco TAC Web Site. The Cisco TAC Web Site requires a Cisco.com login ID and password. If you have a valid service contract but do not have a login ID or password, go to the following URL to register:
http://www.cisco.com/register/
If you cannot resolve your technical issues by using the Cisco TAC Web Site, and you are a Cisco.com registered user, you can open a case online by using the TAC Case Open tool at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/tac/caseopen
If you have Internet access, it is recommended that you open P3 and P4 cases through the Cisco TAC Web Site.
The Cisco TAC Escalation Center addresses issues that are classified as priority level 1 or priority level 2; these classifications are assigned when severe network degradation significantly impacts business operations. When you contact the TAC Escalation Center with a P1 or P2 problem, a Cisco TAC engineer will automatically open a case.
To obtain a directory of toll-free Cisco TAC telephone numbers for your country, go to the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
Before calling, please check with your network operations center to determine the level of Cisco support services to which your company is entitled; for example, SMARTnet, SMARTnet Onsite, or Network Supported Accounts (NSA). In addition, please have available your service agreement number and your product serial number.
This document is to be used in conjunction with the documents listed in the "Documentation Roadmap" section.

Copyright © 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Wed Oct 2 19:22:31 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.